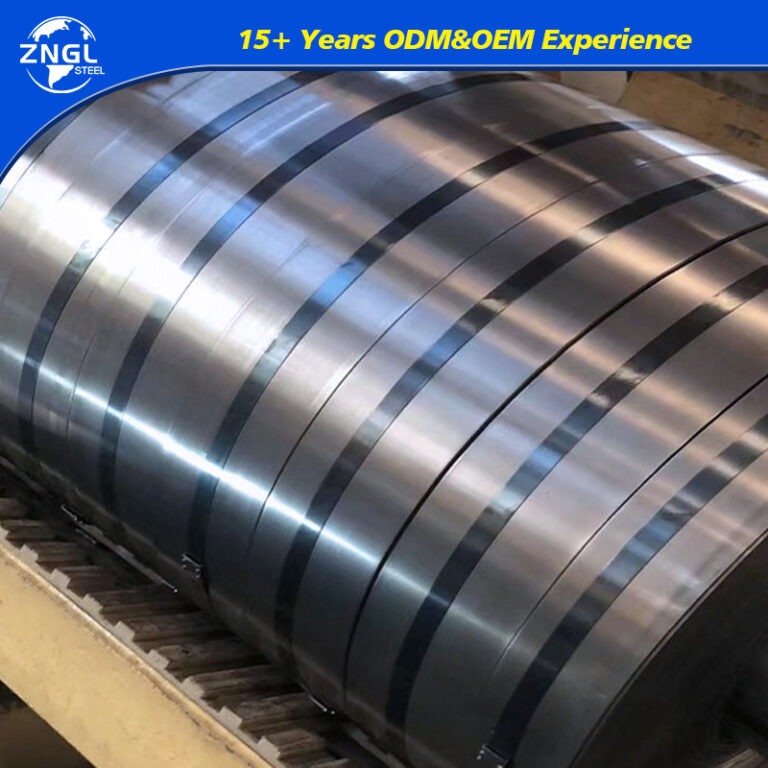
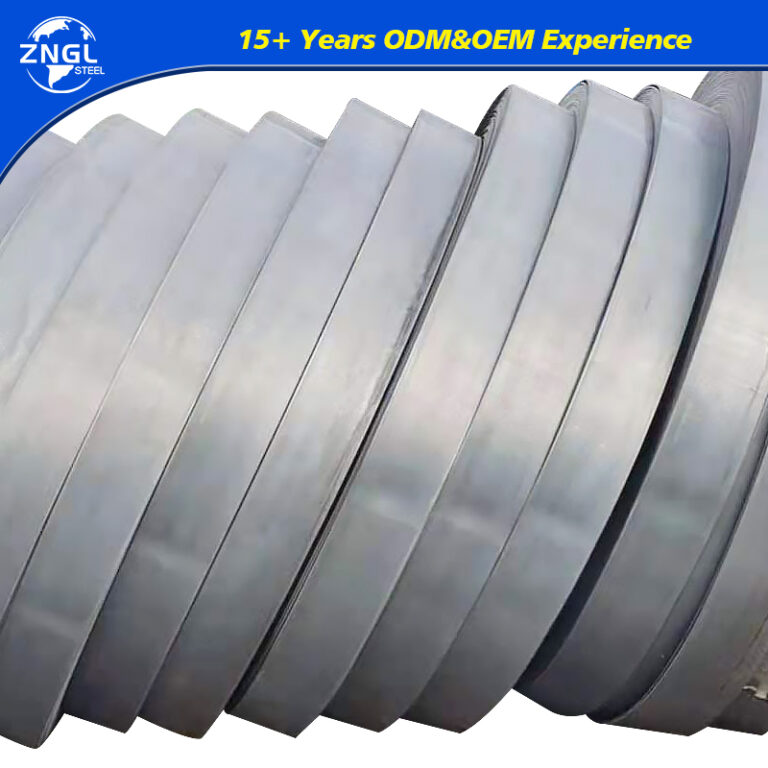
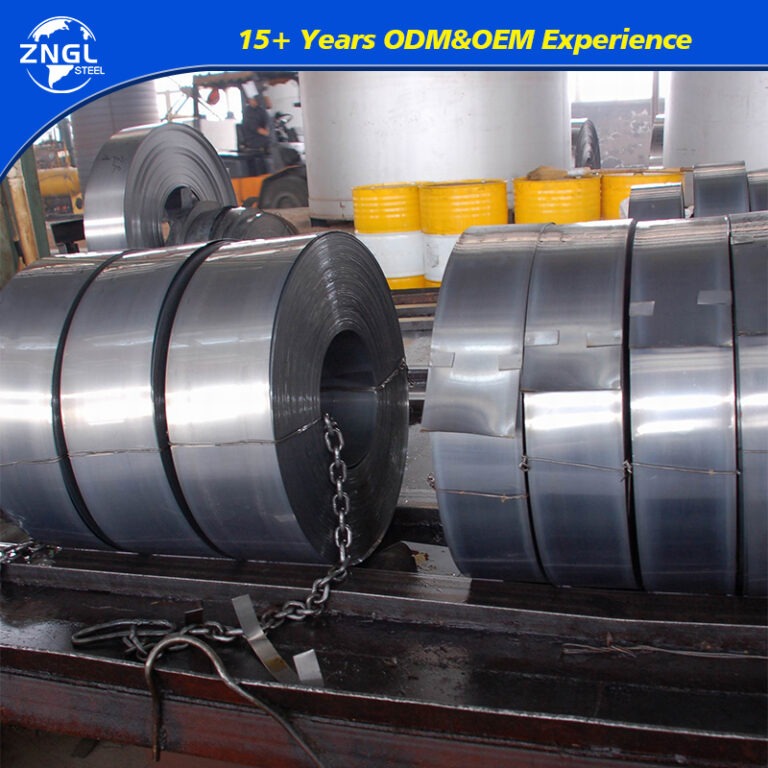
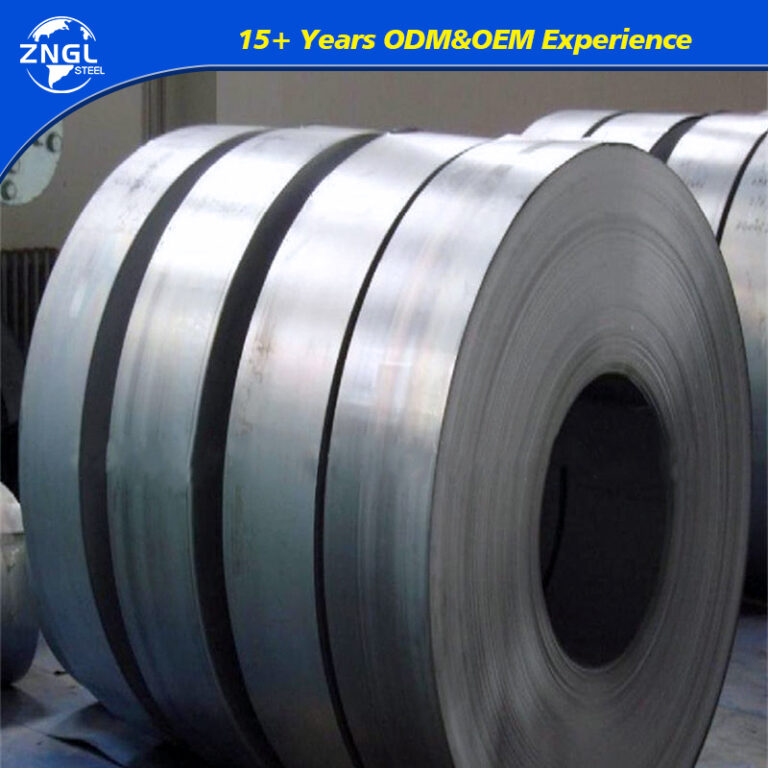
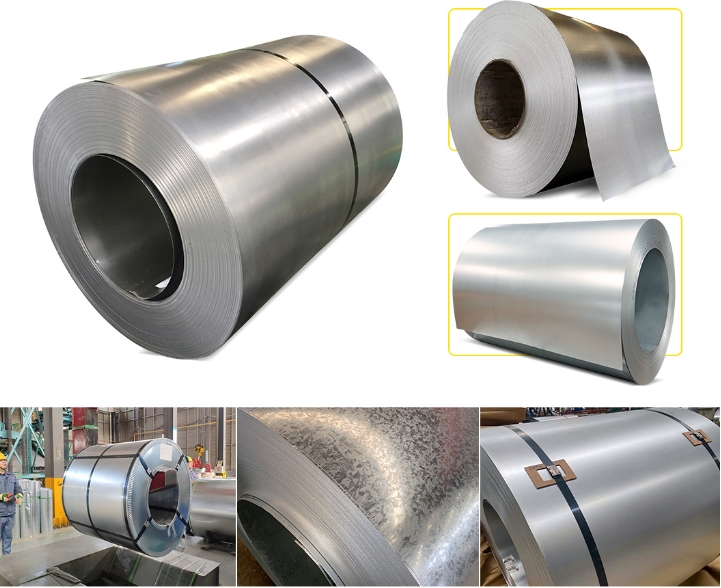
Specifications for Galvanized Coil
| Specifications and Details | |
| Material | CGCC,SGCH,G350,G450,G550,DX51D,DX52D,DX53D |
| Width | 20-1500mm |
| Zinc Coating | Z40-275g/㎡ |
Painting Coating | Top:15 to 25 um(5 um+ 12-20 um) back:7 +/- 2um |
Painting | Nippon,KCC,AkzoNobel,etc |
Coating Type | PE,SMP,HDP,PVDF |
| Resin Con-structure | Double painting and double baking process |
| Back Side Coating Color | Light grey,white and so on |
Coil ID | 508/610MM |
Coil Weight | 3-5 Tons |
Hardness | Soft hard(60),medium hard(HRB60-85),full hard(HRB85-95) |

Key point
- Corrosion Resistance: The zinc coating on galvanized coils offers excellent protection against rust, making them ideal for environments with high moisture and corrosive elements.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Galvanized coils can be painted or coated, allowing for customization in construction and manufacturing projects.
- Durability: The strong bond between steel and zinc ensures that galvanized coils are highly durable, withstanding harsh conditions with minimal maintenance.
- Cost-Effective: Galvanized coils provide a balance of quality and affordability, making them a cost-effective choice for various applications.
Heat Treatment Process
- Annealing: In the production of PPGI, steel is often annealed to soften it before further processing. Annealing involves heating the steel to a temperature between 760-790°C (1400-1450°F) and then slowly cooling it in a furnace to 480°C (900°F) before allowing it to air cool to room temperature. This process makes the steel easier to work with, ensuring it can be easily formed, coated, and painted.
- Hardening: While hardening is more relevant to high-strength steel products, understanding this process helps in the context of PPGI. Hardening involves preheating the steel to 400-650°C (750-1200°F) and then raising the temperature to 780-820°C (1440-1500°F) before quenching in oil. This process is designed to achieve the desired hardness in steel products. For PPGI, maintaining a balance between hardness and ductility is key to ensuring the coated steel can withstand various environmental conditions.
- Tempering: Tempering is a critical process in steel treatment, aiming to achieve the right balance between hardness and toughness. Steel is reheated to 150-350°C (300-660°F) depending on the desired outcome, held at this temperature for an hour per inch of thickness, and then air-cooled. For PPGI, the tempering process of the base steel contributes to the durability and flexibility required for its wide range of applications, including roofing, cladding, and appliances.
Applications of Galvanized Coil

- Cutting Tools: O1 steel is ideal for manufacturing various cutting tools, including knives, punches, and dies due to its high wear resistance and edge retention.
- Molds and Dies: Used in injection molds, extrusion dies, and other forming tools where precision and durability are critical.
- Industrial Blades: Commonly used for making industrial blades that require a sharp and long-lasting edge.
- Measuring Tools: Due to its dimensional stability, it is used in precision measuring tools like gauges and micrometers.











