Mild Steel: A Staple in Structural Engineering
Mild steel, also known as low carbon steel, is a fundamental material in structural engineering due to its excellent properties and cost-effectiveness. This blog post explores the advantages of using mild steel in structural applications and its significance in modern construction.
What is Mild Steel?
Mild steel contains a low carbon content, typically less than 0.3%, which gives it excellent ductility and malleability. It is easy to work with and weld, making it a popular choice for a wide range of structural applications.
Key Properties of Mild Steel
- Ductility and Malleability: The low carbon content in mild steel provides high ductility and malleability, allowing it to be easily formed into various shapes without breaking.
- Weldability: Mild steel’s excellent weldability makes it ideal for construction projects where strong, reliable joints are essential.
- Strength and Toughness: Despite its low carbon content, mild steel offers sufficient strength and toughness for many structural applications, ensuring durability and longevity.
Applications of Mild Steel in Structural Engineering
Mild steel is used extensively in various structural engineering applications due to its versatility and reliability:
- Building Frames: Mild steel is commonly used for constructing building frames, providing a robust and stable skeleton for both residential and commercial structures.
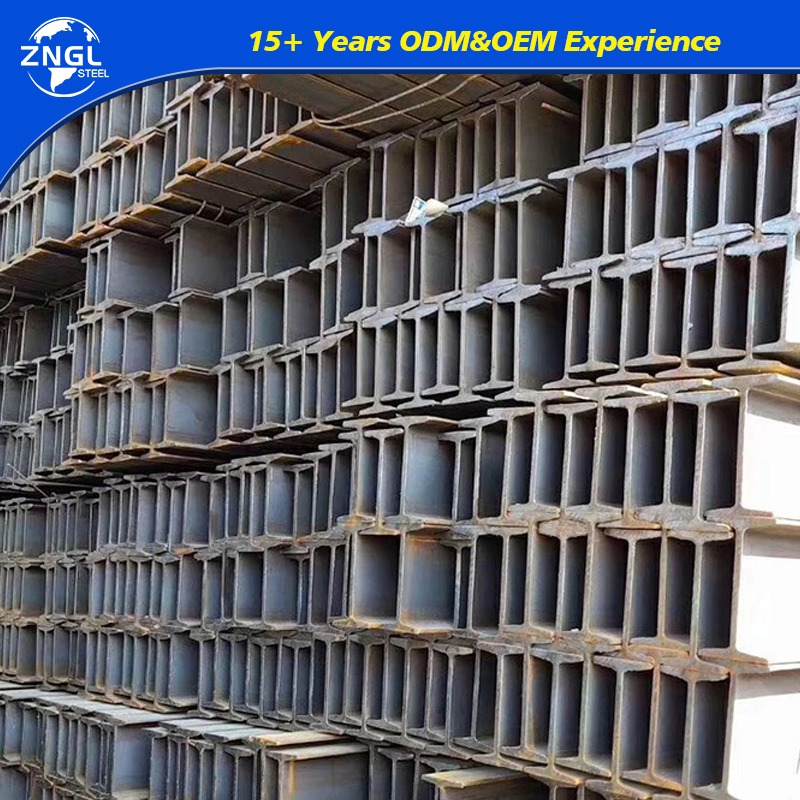
- Beams and Columns: The strength and durability of mild steel make it ideal for beams and columns in buildings, supporting significant loads and providing structural integrity.
- Reinforcement Bars: Mild steel reinforcement bars (rebars) are used in concrete construction to improve tensile strength and reduce cracking.
- Bridges and Infrastructure: Mild steel is widely used in the construction of bridges and other infrastructure projects due to its excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental factors.
Benefits of Using Mild Steel in Structural Applications
- Cost-Effective: Mild steel is relatively inexpensive compared to other construction materials, making it an economical choice for large-scale projects.
- Ease of Fabrication: The ductility and malleability of mild steel make it easy to fabricate, reducing manufacturing costs and time.
- Recyclability: Mild steel is highly recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly choice for sustainable construction practices.
- Versatility: Mild steel can be used in a wide range of applications, from small residential buildings to large industrial structures.
Conclusion
Mild steel is a staple in structural engineering due to its cost-effectiveness, versatility, and excellent mechanical properties. Its widespread use in construction projects underscores its importance in modern engineering practices. Understanding the advantages and applications of mild steel can help professionals make informed decisions when selecting materials for their projects, ensuring structural integrity and longevity.